XmR Trend Chart Formulas
QI Macros can calculate them for you!
Create an XmR Trend Chart using QI Macros
- Select your data.
- Select XmR Trend on QI Macros menu.
- QI Macros will do the math and draw the graph for you.
Go Deeper
The XmR Trend Chart can help you evaluate process performance using variable data when there is only one measurement per period and the data may contain trends (e.g. increasing cost due to inflation, decreasing cost due to technology, etc).
Formulas for the XmR Trend Chart in QI Macros.
Range Chart
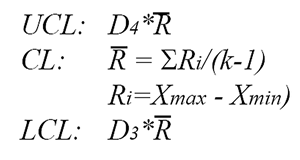
Trend Chart
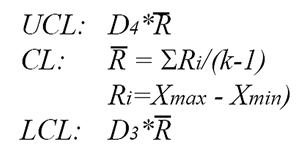
The center line (CL) is calculated using linear regression to give you the slope of the trend and a y-intercept value: "b", calculated as follows:
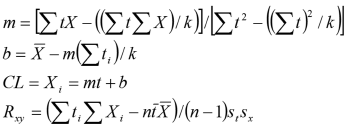
time(i) = ti = 1,2,3,4....k for each X value
m = slope
b = intercept
The XmR Trend then calculates the linear correlation coefficient (Ryx) for the degrees of freedom (df = k-2).
If Ryx is greater than the probability for this degree of freedom, you have a "significant correlation" between x and y. (Probability that you will conclude there is no correlation when there is one = alpha = 0.05).
If Ryx2 is greater than 0.80, then the correlation indicates a "useful fit."
What does this mean?
Significant Correlation - A measure of x versus y. Is the relationship between x and y statistically significant? This is a measure of how well the trend line reflects the relationship between x and y.
Useful Fit - Even if there is a significant correlation above this asks the question - Is it useful? Can I make an assumption or prediction about y based on past history?
A measure of the variation in x vs the variation in y.
This is a measure of how the points vary within the control limits.
Probability - This value comes from the "critical values for the linear correlation coefficient." Said probabilities are derived from the following table for alpha = 0.05. If a calculated value of Ryx is larger or equal to said table value, there is a statistically significant correlation between x and y. And alpha is the probability that we will conclude that there is not a correlation when there actually is one. degrees of freedom = n-2, where n = number of paired samples:
| df | Probability | df | Probability |
| 1 | .997 | 11 | .553 |
| 2 | .950 | 12 | .532 |
| 3 | .878 | 13 | .514 |
| 4 | .811 | 14 | .497 |
| 5 | .754 | 15 | .482 |
| 6 | .707 | 16 | .468 |
| 7 | .666 | 17 | .456 |
| 8 | .632 | 18 | .444 |
| 9 | .602 | 19 | .433 |
| 10 | .576 | 20 | .423 |
| df | Probability | df | Probability |
| 21 | .413 | 35 | .325 |
| 22 | .404 | 40 | .304 |
| 23 | .396 | 45 | .288 |
| 24 | .388 | 50 | .273 |
| 25 | .381 | 60 | .250 |
| 26 | .374 | 70 | .232 |
| 27 | .367 | 80 | .217 |
| 28 | .361 | 90 | .205 |
| 29 | .355 | 100 | .195 |
| 30 | .349 |
(Source: Statistical Methods for the Process Industries, W. McNeese, ASQ Quality Press, Milwaukee)
The XmR Trend Chart is just one of the tools included in QI Macros SPC Software for Excel.
Stop Struggling with XmR Trend Charts!
Start creating your XmR Trend Charts in just minutes.
Download a free 30-day trial. Get XmR Trend Charts now!
Why Choose QI Macros Over Other Control Chart Software?
![]()
Fast and Easy to Use
- Works right in Excel
- Create charts in seconds
- Easy to customize & share charts
- Free Training Anytime
![]()
Proven and Trusted
- More than 100,000 users
- In More than 80 countries
- Five Star CNET Rating - Virus free
![]()
Affordable
- Only $369 USD
Quantity Discounts Available - No annual subscription fees
- Free technical support

